To plot a graph using our dataset is a very crucial part of our prediction. It is not important to fit a straight line, it could also be a polynomial equation. We can have polynomial equations in a graph known as polynomial regression, for example, quadratic function as well as cubic function.
While fitting a particular type of polynomial equation, we have to make sure that our range of different chosen features in our equation must be in the same range.
NORMAL EQUATION
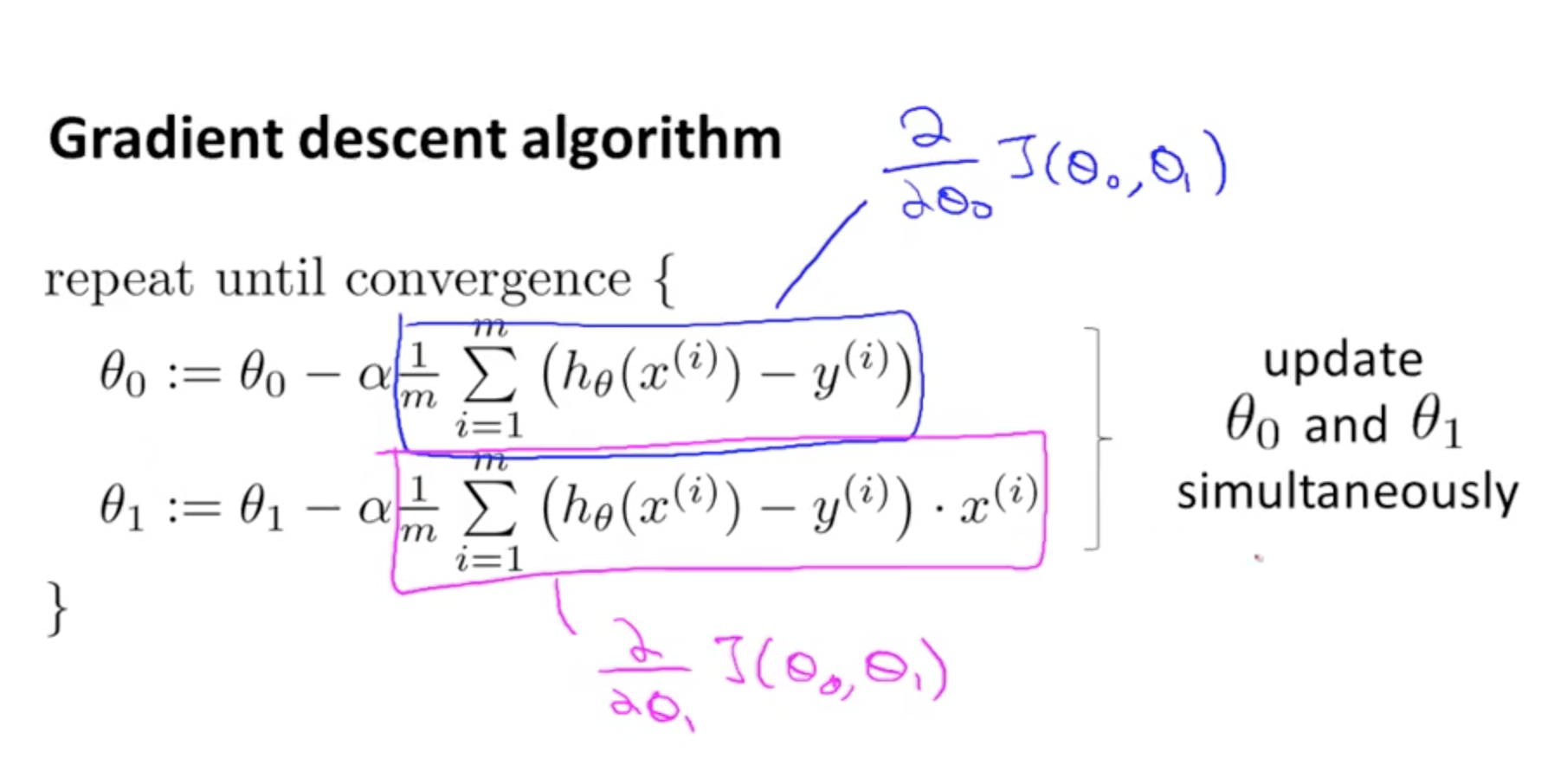
One way of minimizing J is Gradient Descent which takes the approach of the iterative algorithm, another way to reduce the use of this tedious procedure is Normal Equation.
In the “Normal Equation” method, we will minimize J by explicitly taking its derivatives concerning the θj ’s, and setting them to zero. This allows us to find the optimum theta without iteration. The normal equation formula is given below:

Also, there is no use of feature scaling in Normal Equation.
This method can reduce the work but it is also possible that (X^T X)^{-1} is non-invertible, the common cause might be:-
- Redundant features, where two features are very closely related (i.e. they are linearly dependent)
- Too many features (e.g. m ≤ n).
With this, that’s the end of week-2.